共计 6760 个字符,预计需要花费 17 分钟才能阅读完成。
一. 单表查询完整语法
1. 书写的语法顺序
- select
- distinct
- from
- where
- group by
- having
- order by
- limit
2. 完整语法
select [字段 1, 字段 2...] from [表名]
where [条件]
group by [字段]
having [分组后的过滤条件]
order by [排序字段 + 顺序]
limit [显示条数];
二. 关键字执行的优先级
关键字的优先级是帮助你 正确且高效查询数据 的前提, 需要重点了解
- from : 从哪个表来查询 (必须设置)
- where : 设置过滤条件, 查找符合条件的记录 (未设置默认 true, 全部通过)
- group by : 对过滤后的数据按字段进行分组 (如果没有设置, 则整体是一个分组)
- having : 将分组后的结果再进行过滤 (未设置则默认全通过)
- select : 执行 select 执行查找 (必须设置)
- distinct : 去重, 完全一样的数据才可以去重, 去重时应略过主键(非空且唯一) (非必须)
- order by : 对去重后的数据再按照要求排序 (非必须)
- limit : 限制显示或者打印数据的条数 (非必须)
关键字有些可写, 有些可不写, 需要我们自己灵活运用, 下面将介绍使用方法, 派大星 gogogo...
三. 创建表并插入记录(演示准备)
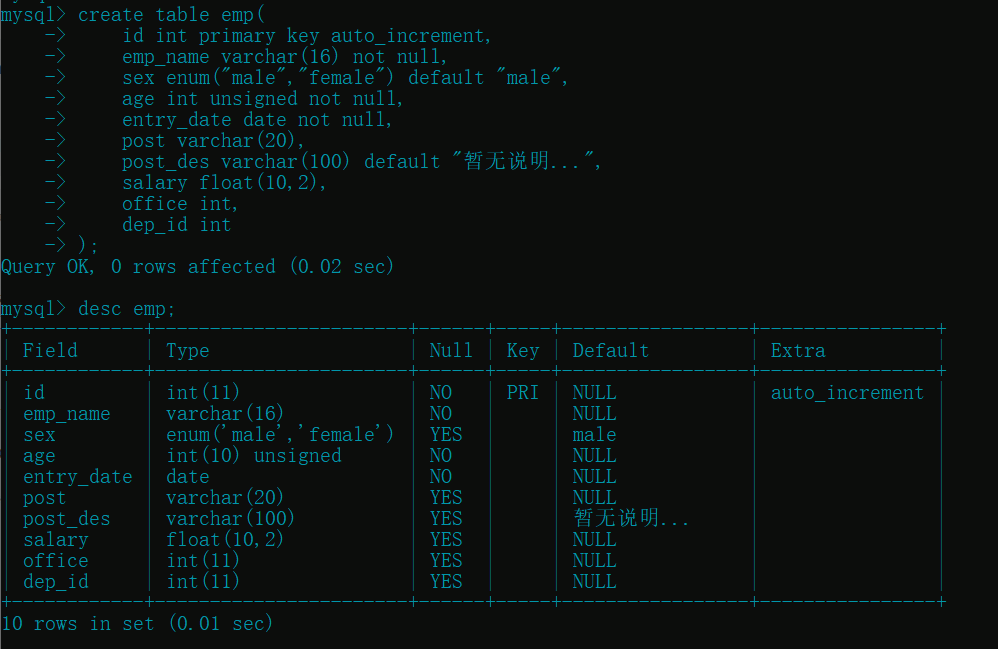
1. 创建一个表
- id, 姓名, 性别, 年龄, 入职日期, 岗位, 岗位描述, 薪资, 办公室, 部门 id
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
emp_name varchar(16) not null,
sex enum("male","female") default "male",
age int unsigned not null,
entry_date date not null,
post varchar(20),
post_des varchar(100) default " 暂无说明...",
salary float(10,2),
office int,
dep_id int
);
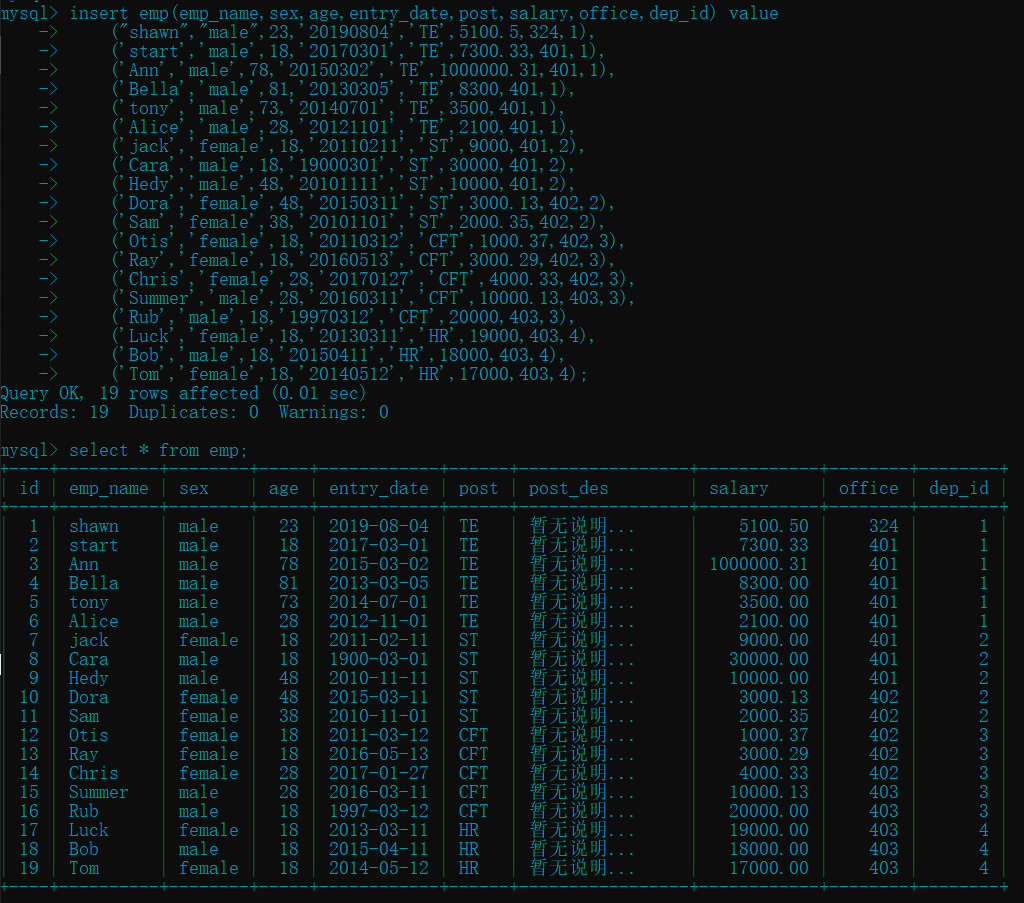
2. 插入员工信息
- 四个部门 : TE、ST、CFT、HR
insert emp(emp_name,sex,age,entry_date,post,salary,office,dep_id) value
("shawn","male",23,'20190804','TE',5100.5,324,1), # 测试工程师
('start','male',18,'20170301','TE',7300.33,401,1),
('Ann','male',78,'20150302','TE',1000000.31,401,1),
('Bella','male',81,'20130305','TE',8300,401,1),
('tony','male',73,'20140701','TE',3500,401,1),
('Alice','male',28,'20121101','TE',2100,401,1),
('jack','female',18,'20110211','ST',9000,401,2), # 系统工程师
('Cara','male',18,'19000301','ST',30000,401,2),
('Hedy','male',48,'20101111','ST',10000,401,2),
('Dora','female',48,'20150311','ST',3000.13,402,2),
('Sam','female',38,'20101101','ST',2000.35,402,2),
('Otis','female',18,'20110312','CFT',1000.37,402,3), # 程式测试工程师
('Ray','female',18,'20160513','CFT',3000.29,402,3),
('Chris','female',28,'20170127','CFT',4000.33,402,3),
('Summer','male',28,'20160311','CFT',10000.13,403,3),
('Rub','male',18,'19970312','CFT',20000,403,3),
('Luck','female',18,'20130311','HR',19000,403,4), # 人力资源
('Bob','male',18,'20150411','HR',18000,403,4),
('Tom','female',18,'20140512','HR',17000,403,4);
准备工作好了, 下面依次来介绍关键字的用法
四.from (来自)
这个比较简单, 就是你想看那张表的数据, from 后面接一个表名
select * from t01;

五.where (条件约束)
设置条件, 对符合条件的数据放行, 未设置默认true, 全部通过
1.where 关键字中可用的操作
- 比较运算符 : >, <, >=, <=, =, !=
- 逻辑运算符 : and, or, not
- Null 判断 : is null, is not null
- 范围查询 : in, between...and
- 模糊查询 : like
- 正则匹配 : regexp
2. 比较、逻辑运算符、范围查询演示
- in : 用于离散型
- between...and : 用于连续区间, 闭区间
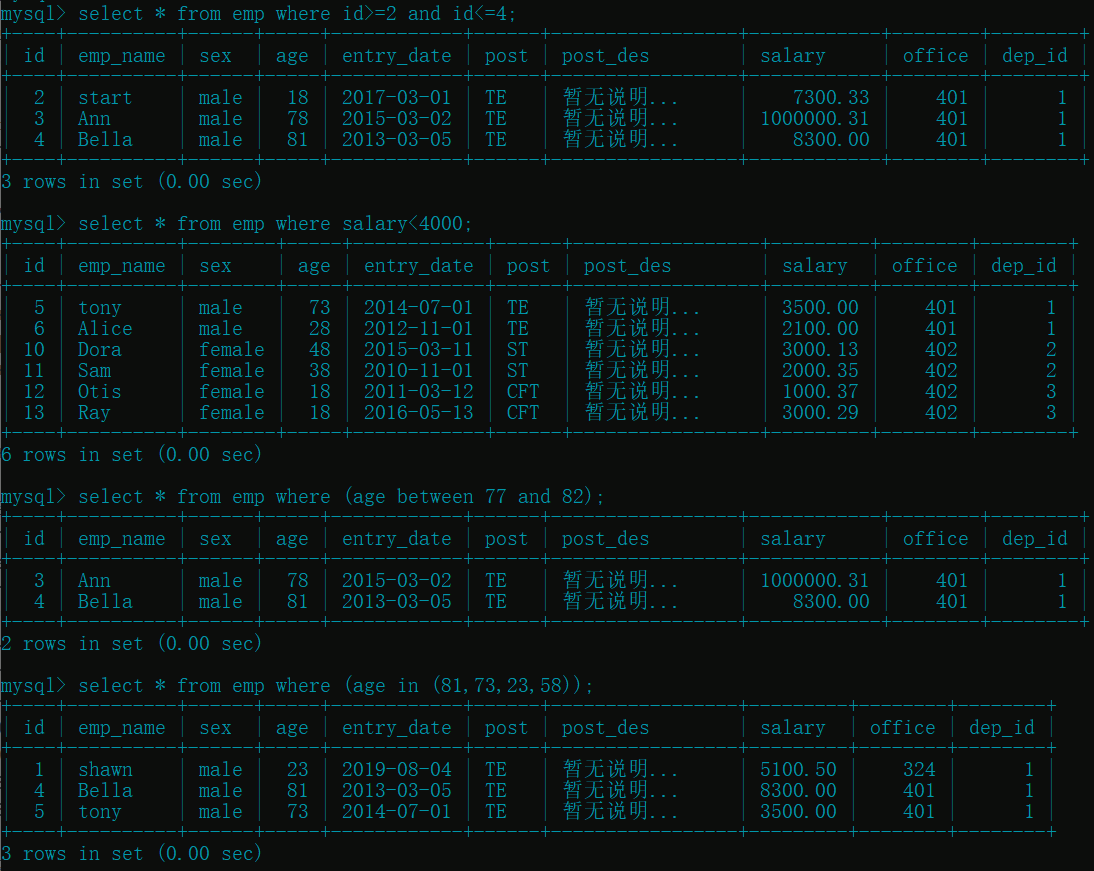
select * from emp where id>=2 and id<=4; # id 2~4 之间的员工闭区间
select * from emp where salary<4000; # 薪资小于 4000 的
select * from emp where (age between 77 and 82); # 年龄在 77~82 之间的, 闭区间(括号可以省略)
select * from emp where (age in (81,73,23,58)); # 年龄在给定值之内的员工
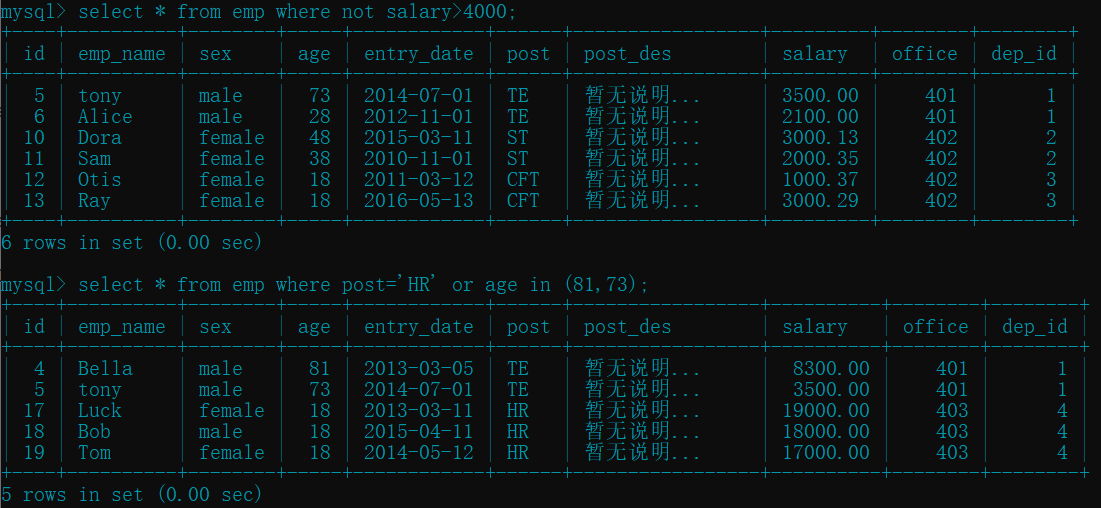
select * from emp where not salary>4000; # 薪資不大于 4000 的员工
select * from emp where post='HR' or age in (81,73); # 岗位 "HR" 或者年龄是指定的员工
3.Null 判断演示
-
is null : 空
-
is not null : 非空
insert emp(emp_name,sex,age,entry_date,post,salary,office) value
("shawn","male",23,'20190804','TE',5100.5,324); # 表里面没有 null 的记录, 我们模拟一条
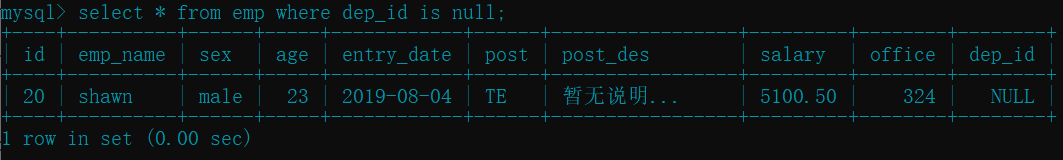
select * from emp where dep_id is null; # 部门编号为空的员工
select * from emp where post is not null; # 岗位不为空的员工
4. 模糊查询演示
- 语法 :
like [符号] - % : 匹配任意多个字符
- _ : 匹配任意单个字符
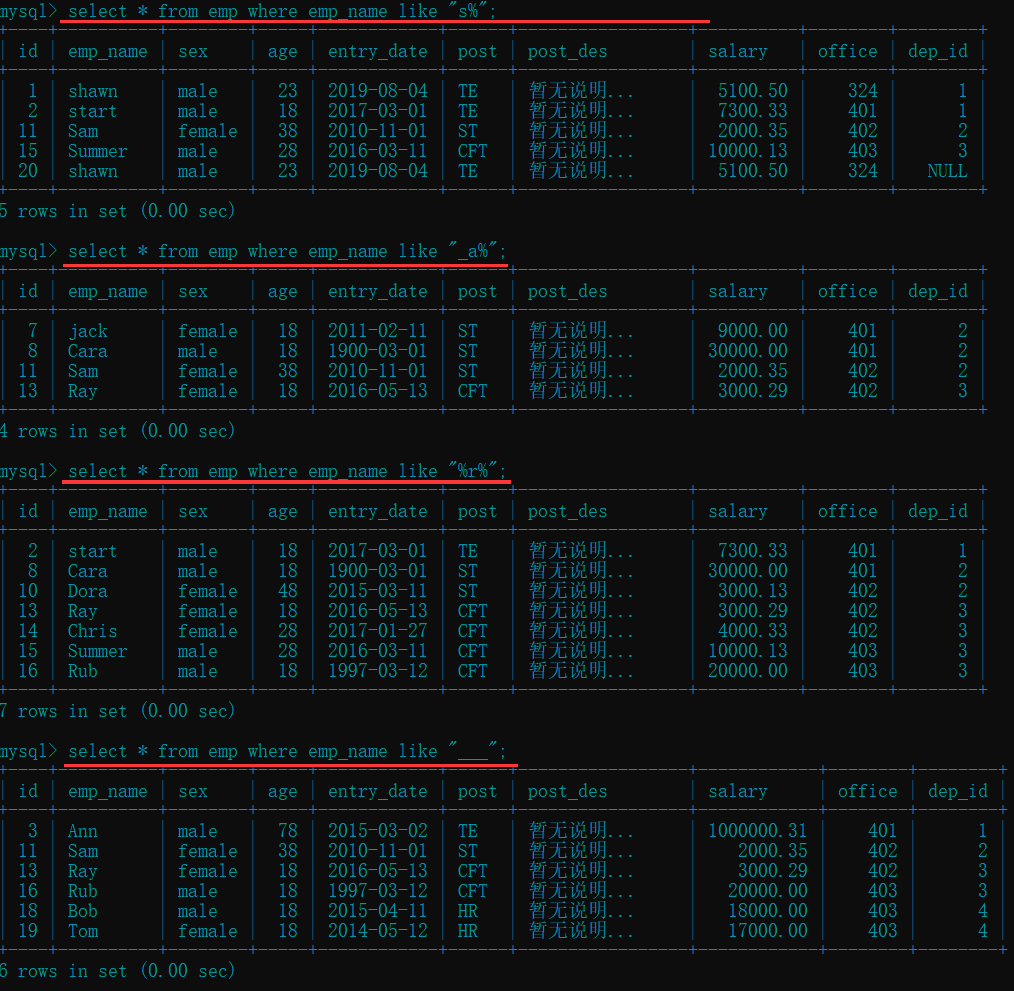
select * from emp where emp_name like "s%"; # 匹配以 "s" 开头的员工(不区分大小写)
select * from emp where emp_name like "_a%"; # 匹配第二个字母为 "a" 的员工
select * from emp where emp_name like "%r%"; # 匹配名字中含有 "r" 的员工
select * from emp where emp_name like "___"; # 匹配名字中有三个字符的员工
5. 正则匹配演示
正则表达式的使用更加强大和灵活, 它是各种语言通用的强大工具, 前面写过一篇 关于正则使用 的博客
- 语法 :
regexp [正则字符]
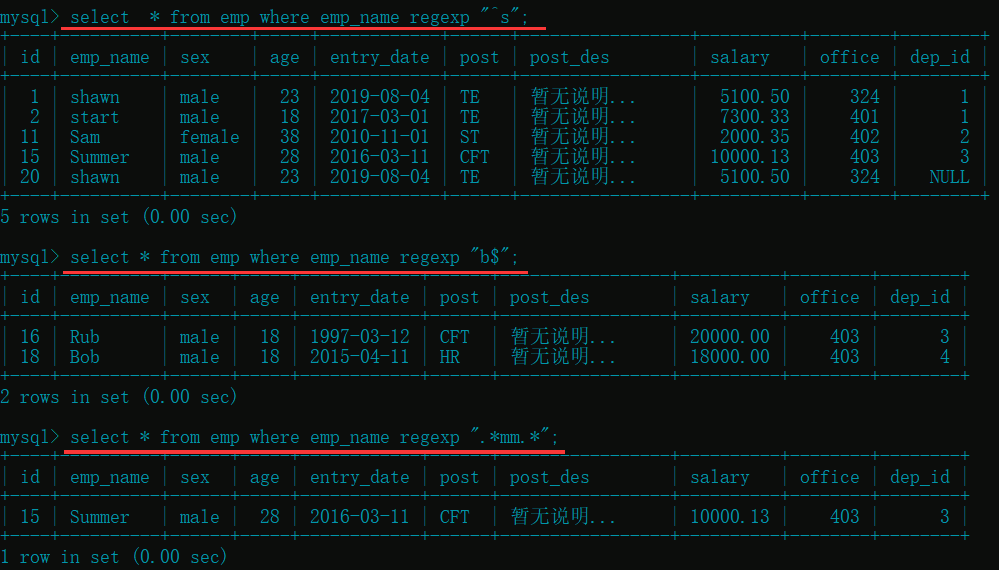
select * from emp where emp_name regexp "^s"; # 匹配 "s" 开头名字的员工
select * from emp where emp_name regexp "b$"; # 匹配 "b" 结尾名字的员工
select * from emp where emp_name regexp ".*mm.*"; # 匹配含有 "mm" 字符名字的员工
六.group by (分组)
group by 分组在 where 过滤之后执行
1. 分组的作用
目的是为了统计分析每个组内的数据信息, 比如部门人数、岗位人数、男人数、女人数、平均薪资、平均年龄等
2. 使用注意
- 如果我们使用 主键 或者 unique 的字段为一组, 那么表中的每一条记录都自成一组, 这样做毫无意义, 所以使用 group by 分组的时候应该略过主键和 unique 字段
- 分组后只能使用分组后的字段, 如果需要查看组内的信息, 可以使用 聚合函数
3. 聚合函数
- max() : 求最大值
- min() : 求最小值
- sum() : 求和
- avg() : 求平均值
- count() : 统计记录的条数
- group_concat() : 将来自同一组的某一列 (或者多列) 的数据连接成一个字符串
- concat() : 不分组时使用, 可以对查询出来的字段进行额外的拼接操作
- concat_ws() : 不分组时使用, 可以对查询出来的字段进行额外的拼接操作
- case 语句 : 不分组是使用
聚合函数后边可用
as来取别名 :max(xxx) as [别名], 也可以省略as, 例如 :max(xxx) [别名], 还可以为表取别名 :...emp as t01, 但是得注意, 表别名之后, 使用表名也就换成了表别名
4. 以某字段分组演示
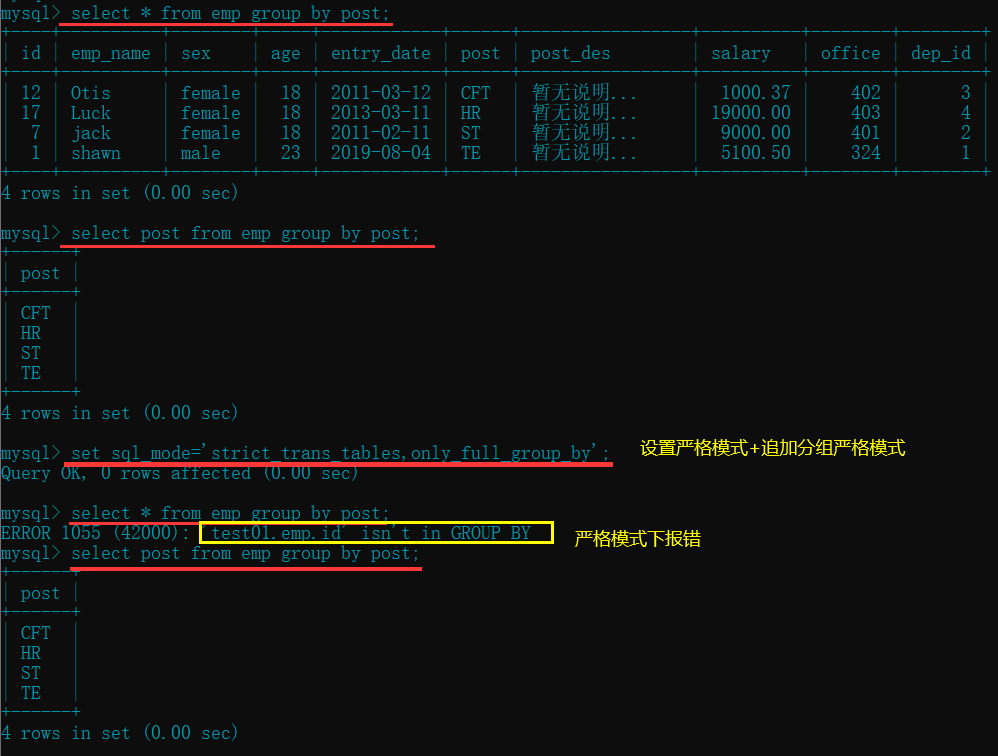
select * from emp group by post; # 以部门为分组字段🔴(没有设置严格模式, 会取每一个部门的第一个员工)
select post from emp group by post; # 指定字段不会出现上面的情况
set sql_mode='strict_trans_tables,only_full_group_by'; # 设置严格模式 + 追加分组严格模式
select * from emp group by post; # 设置严格模式之后再使用这种方式直接报错
select post from emp group by post; # 还是指定字段分组
5. 配合聚合函数使用演示
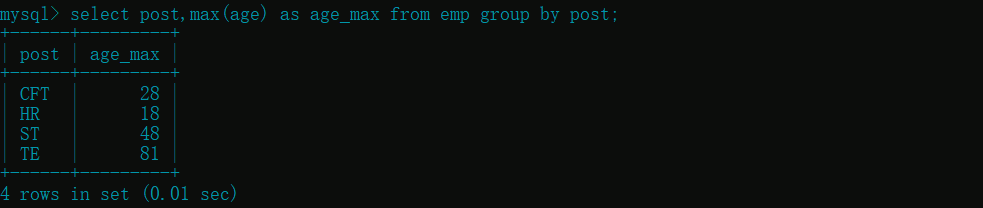
- 查询每个部门的最大年龄 :
max()
select post,max(age) as max_age from emp group by post;
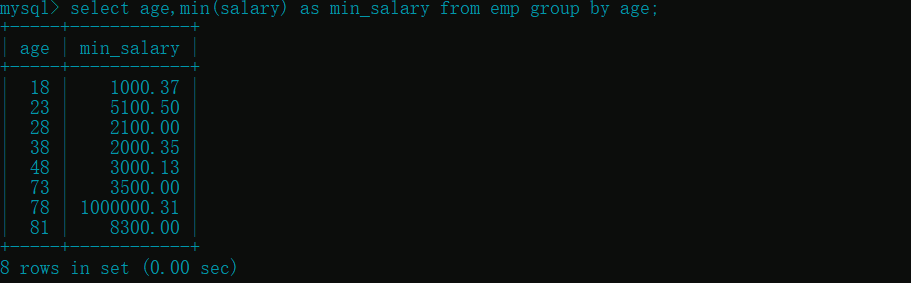
- 查看每个年龄员工的最低工资 :
min()
select age,min(salary) as min_salary from emp group by age;
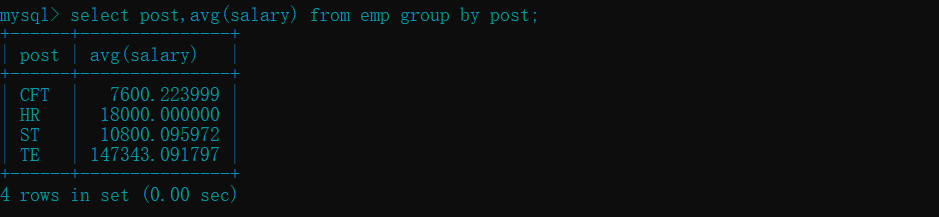
- 查看每个部门的平均工资 :
avg()
select post,avg(salary) from emp group by post;
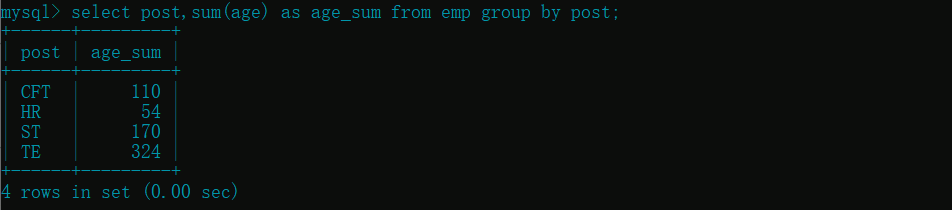
- 查看每个部门的年龄总和 :
sum()
select post,sum(age) as age_sum from emp group by post;
- 查看每个部门的人数 :
count()
select post,count(id) as post_people from emp group by post;
# count() 函数最好使用可以表示唯一性的字段, 入所演示的 id 就是唯一性的字段(当然其他字段也可以)
# 特别注意的是不能使用有 null 关键字的字段
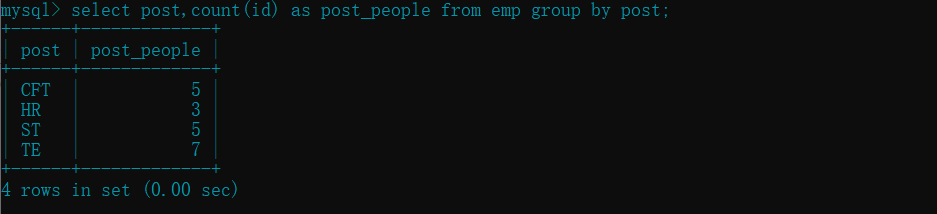
- 查询每个部门员工的名字(每个部门一行显示) :
group_concat() - 对每个部门员工名字后拼接字符 "_haha"
- 查询每个部门每个员工的薪资 : "[员工名] : [薪资的形式]"
select post,group_concat(emp_name) from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(emp_name,"_haha") from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(emp_name,":",salary) from emp group by post;
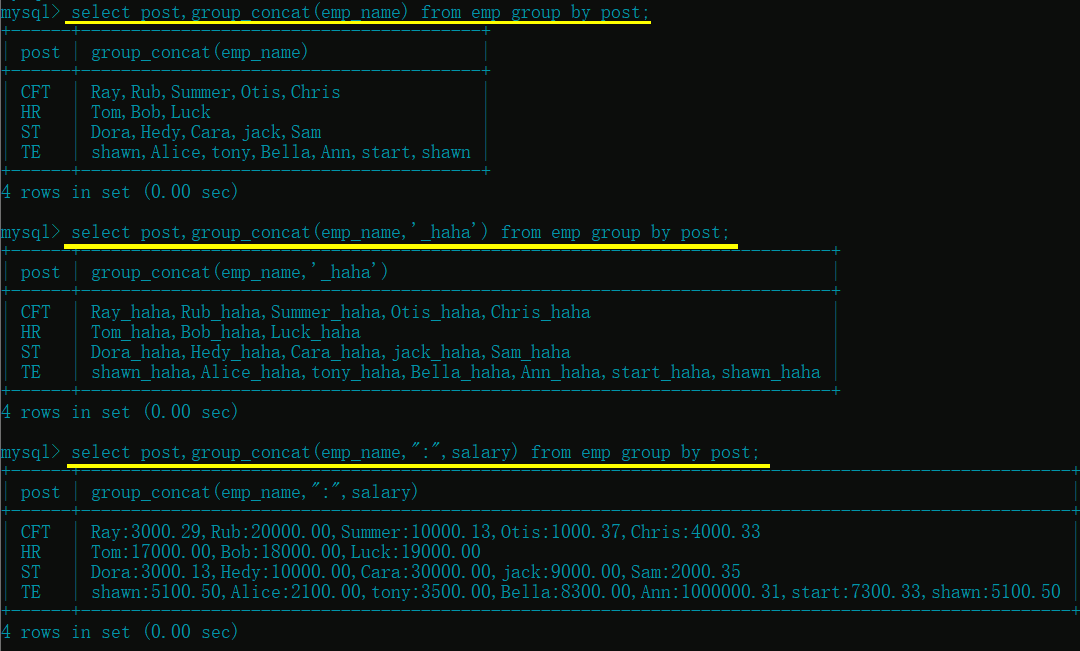
concat(): 注意, 这个是不分组时使用的拼接函数- 查询 id 大于 10 的员工的姓名和年龄
- 查询年龄在 23 岁以上的员工姓名和岗位
select concat("name:",emp_name),concat("age:",age) from emp where id>10;
select concat("name:",emp_name," post:",post) from emp where age>23;

concat_ws([指定的分隔符], [字段 1],[字段 2]...)- 上面 concat() 拼接字段的时候, 如果有很多字段, 那么就需要手动输入许多分隔符, concat_ws() 只需在前面指定一次即可
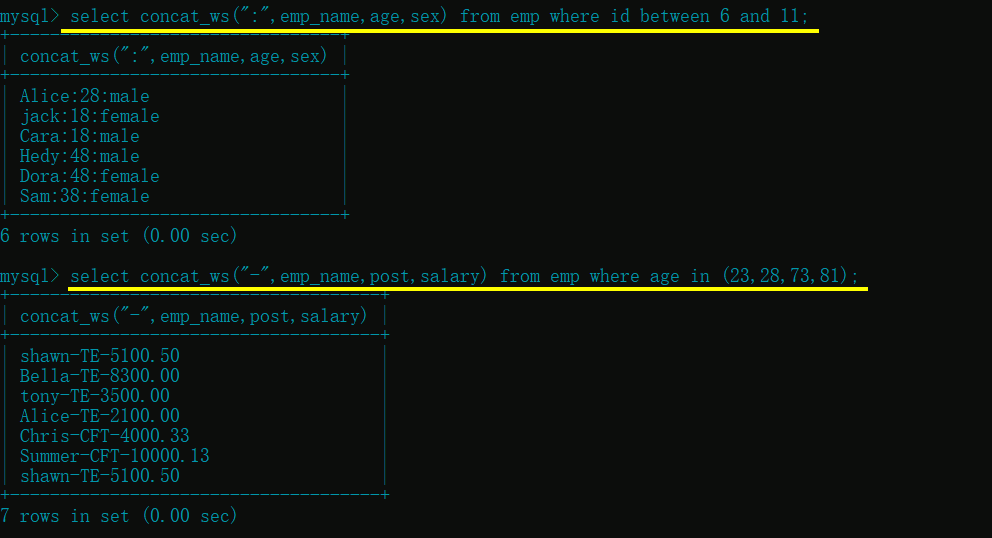
select concat_ws(":",emp_name,age,sex) from emp where id between 6 and 11;
select concat_ws("-",emp_name,post,salary) from emp where age in (23,28,73,81);
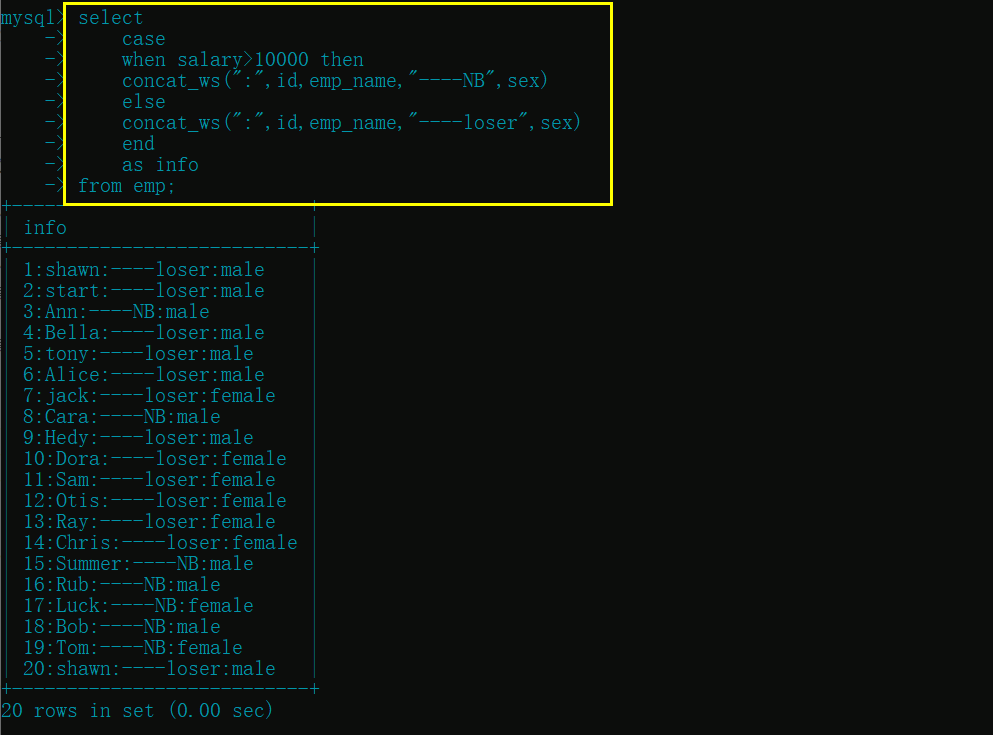
case语句
🥭伪代码
case when [条件 1] then [结果]
when [条件 2] then [结果]
...
else [结果]
end
🥭示例:
#查找薪资大于 10000 的员工, 并对其信息进行拼接 id+ 姓名 ---NB+sex, 小于的 id+ 姓名 ---loser+sex
select
case
when salary>10000 then
concat_ws(":",id,emp_name,"----NB",sex)
else
concat_ws(":",id,emp_name,"----loser",sex)
end
as info
from emp;
聚合函数必须在分组后使用, 不分组默认整张表就是一组
七.having (过滤)
having 是在 group by 之后的筛选操作
1.having 和 where 的区别
- 执行优先级 : where > group by > having
- where 在 group by 之前, 因而 where 中可以有任何字段, 但绝对不能使用聚合函数
- having 发生在 group by 之后, 因而 having 中可以使用分组字段, 无法直接取到其他字段, 可以使用聚合函数
2. 演示
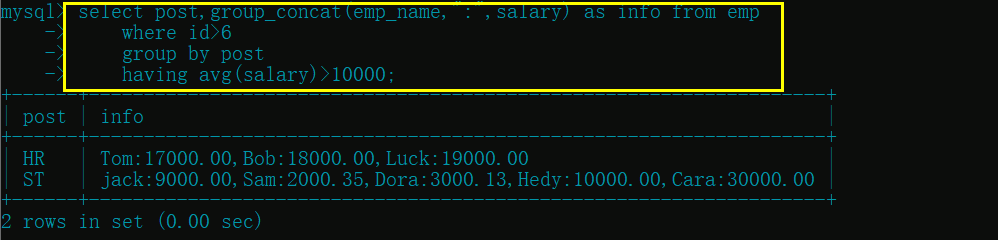
- 统计各部门 id 大于 6 的员工平均工资并保留平均薪资大于 10000 的部门
select post,group_concat(emp_name,":",salary) as info from emp
where id>6
group by post
having avg(salary)>10000;
- 查询各岗位内包含的员工个数小于 2 的岗位名、岗位内包含员工名字、个数
select post,group_concat(emp_name),count(id) from emp
group by post
having count(id)>2;

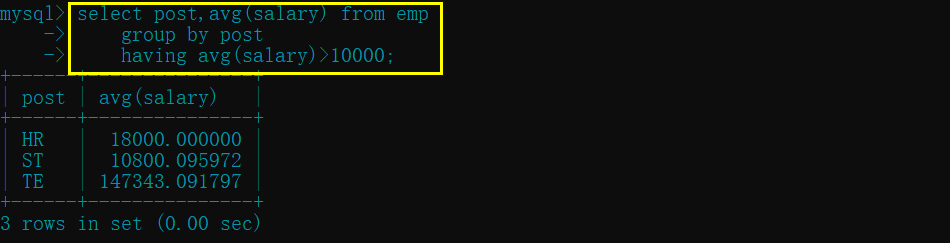
- 查询各岗位平均薪资大于 10000 的岗位名及平均薪资
select post,avg(salary) from emp
group by post
having avg(salary)>10000;
八.distinct (去重)
-
distinct一般是用来去除查询结果中的重复记录的 -
完全一样的数据才可以去重, 去重时应略过主键 (非空且唯一) 和设置了 unique 字段
select distinct age from emp; # 只对一列进行操作
select distinct age,salary from emp; # 对多列进行操作, 多列去重

- 并且
distinct只能放在所有字段前面
select age,distinct salary from emp; # 错误语法, 报错
九.order by (查询排序)
- order by : 默认升序, 后面可以指定
asc asc: 升序,desc: 指定降序- 可以指定多个字段进行多种排序规则
select * from emp order by salary; # 默认升序
select * from emp order by salary asc; # 指定升序
select * from emp order by salary desc; # 指定降序
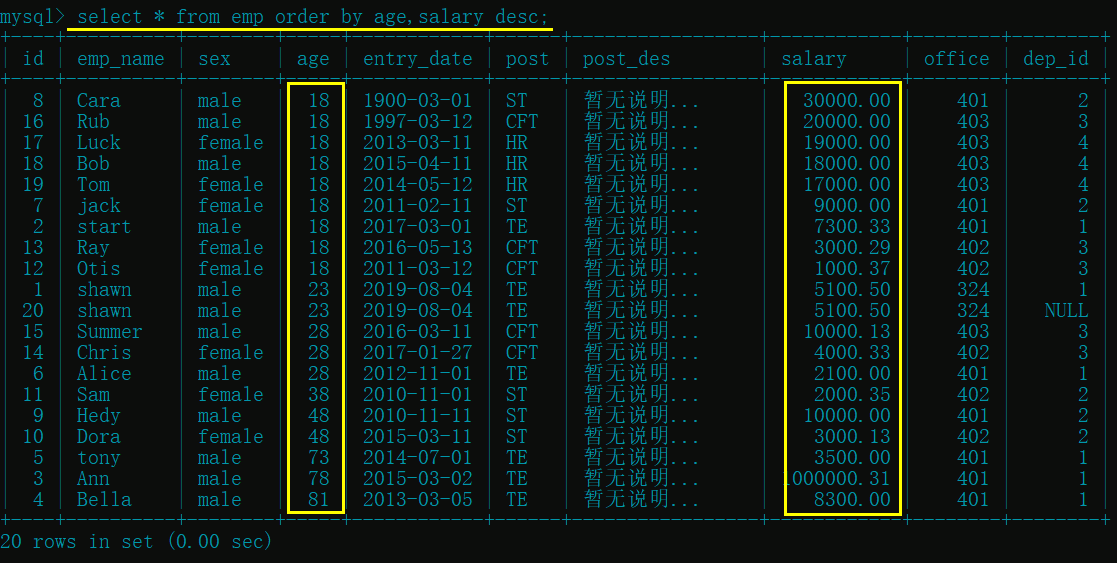
select * from emp order by age,salary desc; # 先 age 升序, 如果有 age 相同的员工, 再进行薪资降序
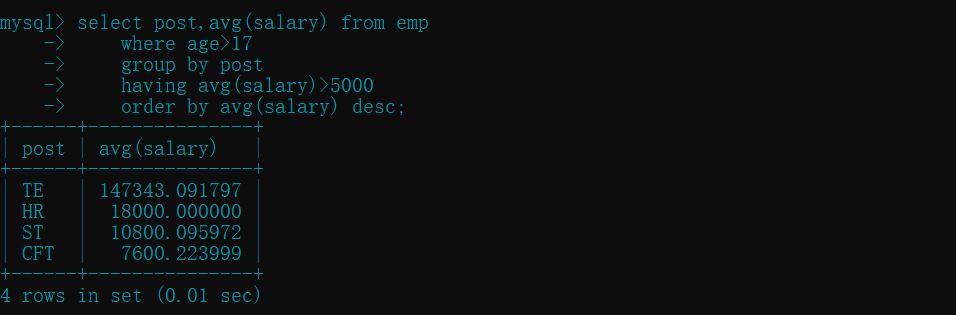
- 统计各部门年龄在 17 岁以上的员工平均工资, 并保留平均工资大于 5000 的部门, 然后对平均工资降序排序
select post,avg(salary) from emp
where age>17
group by post
having avg(salary)>5000
order by avg(salary) desc;
select post,avg(salary) as avg_salary,group_concat(emp_name,":",age) from emp
where age>17
group by post
having avg(salary)>5000
order by avg_salary desc; # select 的优先级大于 order by, 而 as 是在 select 这里别名的, 所以在 order 这里需要使用别名

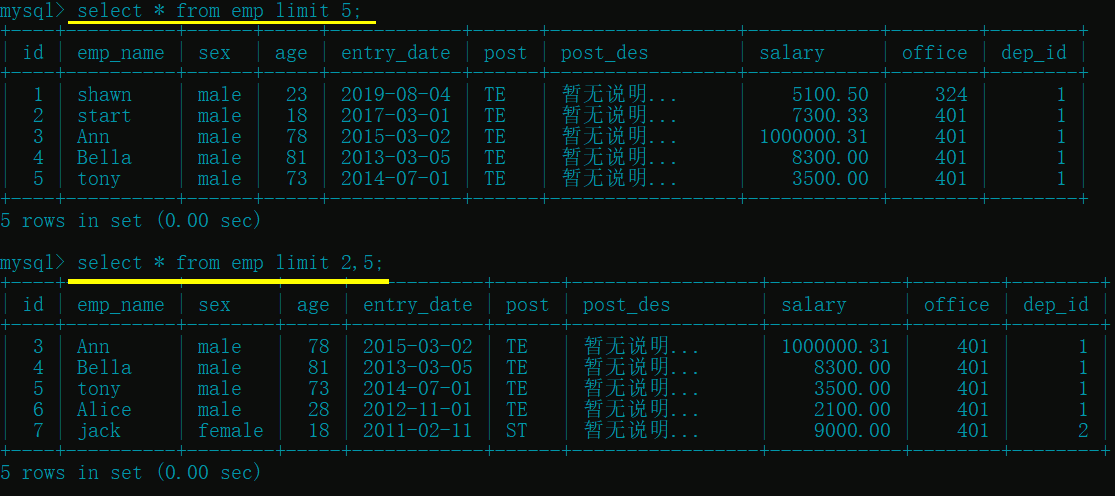
十.limit (限制查询的记录数)
limit 2,5: 第一个参数是起始位置, 第二个参数是展示的条数(只有一个参数代表值展示指定条数数据)
select * from emp limit 5; # 值展示 5 条记录
select * from emp limit 2,5; # 从第 2 条记录开始往后取 5 条记录
----end----
正文完








